Indonesia has emerged as a key player in the global e-commerce market. The rise of e-commerce in Indonesia is a testament to the country’s rapid technological adoption and growing digital economy. This article digs into the growing e-commerce Indonesia, examines the major players, explores consumer behavior trends, addresses logistical challenges, and outlines future prospects.
The Rise of E-commerce in Indonesia
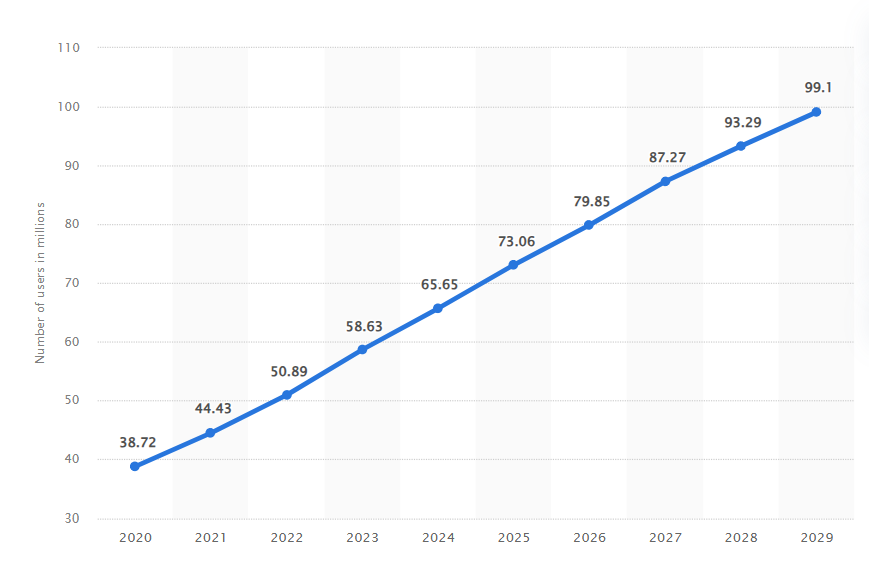
The e-commerce Indonesia landscape has seen exponential growth over the past decade. As the largest economy in Southeast Asia, Indonesia presents a lucrative market for online businesses. The combination of a young, tech-savvy population, increasing internet penetration, and the proliferation of smartphones has created an ideal environment for e-commerce to flourish.
Major Players in E-commerce Indonesia
Several key players dominate the e-commerce Indonesia market:
Tokopedia: Founded in 2009, Tokopedia has grown into one of Indonesia’s largest online marketplaces. It offers a wide range of products, from electronics to fashion, and has a strong focus on empowering small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Tokopedia has also formed a strategic partnership with TikTok, leveraging the social media platform’s massive user base to drive more traffic and sales.
Shopee: Shopee, a subsidiary of Sea Group, has quickly become a major player in Indonesia’s e-commerce scene. Known for its user-friendly app and aggressive marketing strategies, Shopee has captured a significant share of the market.
Lazada: Backed by Alibaba Group, Lazada leverages strong logistical capabilities and extensive product offerings to attract Indonesian consumers.
Carousel: Carousel is gaining traction in Indonesia by providing a platform for buying and selling secondhand products. This marketplace caters to consumers looking for affordable, pre-owned items, ranging from electronics to fashion.
Consumer Behavior Trends
The rise of e-commerce in Indonesia is closely tied to evolving consumer behavior. Several trends are driving this growth:
Mobile Shopping: With high smartphone penetration, mobile shopping has become the norm in Indonesia. Consumers prefer the convenience of shopping via mobile apps, leading e-commerce platforms to optimize their mobile interfaces.
Social Commerce: Social media platforms play a significant role in influencing purchasing decisions. Many consumers discover products through social media channels, which has led to the rise of social commerce.
Cashless Transactions: The adoption of digital payment methods, such as e-wallets and online banking, is on the rise. Platforms like GoPay, OVO, and Dana are making transactions easier and more secure, encouraging more consumers to shop online.
Cash on Delivery (COD): Despite the growth of digital payments, Cash on Delivery (COD) remains a popular payment method in Indonesia. Many consumers prefer COD as it offers a sense of security, allowing them to pay only upon receiving their products. However, COD poses challenges for e-commerce platforms, including higher return rates, logistical complexities, and increased risk of payment default.
Diverse Product Range: Indonesian consumers are increasingly seeking a diverse range of products online, from daily necessities to luxury goods. This demand drives e-commerce platforms to continually expand their offerings.
Logistical Challenges
Despite its rapid growth, the e-commerce Indonesia market faces several logistical challenges:
Geographical Complexity: Indonesia’s vast archipelago poses significant logistical challenges. Delivering products to remote islands can be difficult and costly, impacting delivery times and costs.
Infrastructure: While urban areas have well-developed infrastructure, rural areas often lack reliable transportation and delivery networks. This disparity can hinder the reach of e-commerce platforms.
Last-Mile Delivery: The last-mile delivery, or the final step of the delivery process, is often the most challenging. Traffic congestion in urban areas and accessibility issues in rural areas can delay deliveries and increase costs.
COD Challenges: The preference for Cash on Delivery (COD) adds another layer of complexity. Handling cash transactions at the point of delivery increases operational costs and the risk of fraud. Additionally, managing returns and refunds for COD orders can be more cumbersome and resource-intensive.
Future Prospects
The future of e-commerce in Indonesia looks promising. Several factors contribute to its positive outlook:
Technological Advancements: Continued advancements in technology, such as improved internet connectivity and the adoption of artificial intelligence, will enhance the e-commerce experience for consumers and businesses alike.
Government Support: The Indonesian government is actively supporting the digital economy through various initiatives and policies. Efforts to improve infrastructure and streamline regulations will further boost the e-commerce sector.
Increased Investment: Both local and international investors are recognizing the potential of e-commerce in Indonesia. Increased investment in technology, logistics, and digital payment solutions will drive further growth.
Expansion of Market Reach: E-commerce platforms are increasingly targeting rural areas and smaller cities, expanding their reach beyond urban centers. This will open up new markets and drive further adoption.
Conclusion
The rapid growth of e-commerce in Indonesia is a remarkable example of how technological adoption can transform a market. With major players like Tokopedia, Shopee, Lazada, and Carousel leading the way, and evolving consumer behavior trends supporting this growth, the future of e-commerce Indonesia looks bright. While logistical challenges remain, advancements in technology and infrastructure, along with government support, will likely overcome these hurdles, ensuring continued growth and innovation in the sector.

