Indonesia is experiencing a significant transformation in its construction industry, driven by the adoption of green building practices. As the country strives to meet its net-zero carbon emissions target by 2060, sustainable building designs and energy-efficient materials have become central to reshaping the sector. The journey towards a greener construction landscape in Indonesia not only aligns with global sustainability efforts but also promises numerous long-term benefits. Without further ado, let’s take a look at Indonesia Green Building Trends below!
Indonesia Green Building Trends? The Push for Sustainability
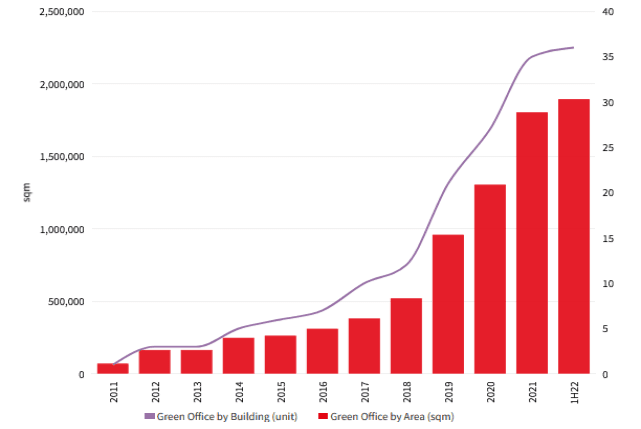
The Indonesian government has made clear commitments to sustainability, starting with the establishment of the Green Building Council Indonesia in 2009. This institution has played a crucial role in driving awareness and supporting the development of Indonesia Green Building Trends.
A pivotal moment came in 2016 when Jakarta, Indonesia’s capital, set a bold goal of reducing energy consumption, water usage, and CO2 emissions by 30% by 2030. To meet these ambitious targets, building owners in Jakarta are required to integrate green building principles into both new and existing structures.
Indonesia Green Building Trends: National Efforts and Goals
Indonesia’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions extends beyond individual cities. The National Development Planning Agency (Bappenas) emphasizes the importance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices in achieving Indonesia’s emission reduction goals. By 2030, Indonesia aims to reduce emissions by 31.89% through domestic measures and 43.20% with international assistance.
Key national programs, including the National Medium-Term Development Plan (RPJMN) for 2020-2024, further underscore the importance of improving environmental quality. Furthermore, it can help enhancing disaster resilience and promoting low-carbon development. These initiatives are critical to advancing the adoption of Indonesia Green Building Trends.
Regulatory Landscape and Challenges
While Indonesia has made strides in green building regulations, there are still challenges to achieving widespread implementation. The government’s Green Building Regulation (GR 16/2021) is a positive step, outlining standards for energy efficiency, water management, and sustainable materials. However, these regulations only apply to large buildings exceeding 5,000 square meters, limiting the reach of these standards. It means the residential sector doesn’t have to comply, although it accounts for 83% of the country’s building energy demand.
A study case done in Semarang illustrates the potential impact of Indonesia Green Building Trends. By improving air conditioning systems and using energy-efficient building materials, energy consumption could be reduced by up to 44%. This could save the city millions of dollars in energy costs each year. However, financing remains a significant hurdle. Meeting Semarang’s green building mandates over the next decade will require an estimated investment of USD 223.7 million, highlighting the need for additional funding to support this transition.
Energy-Efficient Materials and Innovation
A key aspect of Indonesia Green Building Trends is the use of energy-efficient materials. The construction industry is exploring innovative solutions, from recycled and natural materials to low-energy production methods. New technologies, like self-healing concrete and transparent aluminum, are being introduced to improve building durability and energy efficiency. These advanced materials can significantly reduce energy consumption in buildings. As a result, this might lead to long-term environmental benefits.
The adoption of Indonesia Green Building Trends is transforming the construction landscape, offering a promising path towards sustainability. From the government’s ambitious goals to the innovative use of energy-efficient materials, these efforts are reshaping the industry. Not to forget that this can also reduce the country’s environmental footprint. While challenges remain, Indonesia is moving in the right direction. As more cities and corporations embrace these sustainable practices, the future of Indonesian construction looks greener and more sustainable than ever.

